第6章 栈
计算器
剑指offerⅡ36:后缀表达式
根据 逆波兰表示法,求该后缀表达式的计算结果。
有效的算符包括 +、-、*、/ 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
说明:
- 整数除法只保留整数部分。
- 给定逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
示例 1:
输入:tokens = ["2","1","+","3","*"]
输出:9
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) * 3) = 9示例 2:
输入:tokens = ["4","13","5","/","+"]
输出:6
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:(4 + (13 / 5)) = 6示例 3:
输入:tokens = ["10","6","9","3","+","-11","*","/","*","17","+","5","+"]
输出:22
解释:
该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:
((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5
= (0 + 17) + 5
= 17 + 5
= 22逆波兰表达式:
逆波兰表达式是一种后缀表达式,所谓后缀就是指算符写在后面。
- 平常使用的算式则是一种中缀表达式,如
( 1 + 2 ) * ( 3 + 4 )。 - 该算式的逆波兰表达式写法为
( ( 1 2 + ) ( 3 4 + ) * )。
逆波兰表达式主要有以下两个优点:
- 去掉括号后表达式无歧义,上式即便写成
1 2 + 3 4 + *也可以依据次序计算出正确结果。 - 适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中。
算法:
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (String token : tokens) {
switch (token) {
case "+":
case "-":
case "*":
case "/":
int b = stack.pollLast();
int a = stack.pollLast();
stack.offer(calculate(a, b, token));
break;
default:
stack.offer(Integer.parseInt(token));
}
}
return stack.getFirst();
}
private int calculate(int a, int b, String operator) {
switch (operator) {
case "+":
return a + b;
case "-":
return a - b;
case "*":
return a * b;
case "/":
return a / b;
default:
return 0;
}
}
}LC227:基本计算器Ⅱ
给你一个字符串表达式 s ,请你实现一个基本计算器来计算并返回它的值。
整数除法仅保留整数部分。
class Solution {
Deque<Integer> numStack = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<Character> operatorStack = new LinkedList<>();
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public int calculate(String s) {
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
map.put('+', 1);
map.put('-', 1);
map.put('*', 2);
map.put('/', 2);
int length = ch.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (ch[i] == ' ') {
continue;
}
if (isNum(ch[i])) {
int num = 0;
while (i < length && isNum(ch[i])) {
num = num * 10 + ch[i++] - '0';
}
numStack.offer(num);
i--;
System.out.println(i);
} else {
while (!operatorStack.isEmpty() && judge(map, operatorStack.peekLast(), ch[i])) {
numStack.offer(evaluate());
}
operatorStack.offer(ch[i]);
}
}
while (!operatorStack.isEmpty()) {
numStack.offer(evaluate());
}
return numStack.peekLast();
}
private boolean isNum(char ch) {
return ch <= '9' && ch >= '0';
}
//判断栈顶的操作符优先级是否大于等于当前扫描道德操作符优先级
private boolean judge(Map<Character, Integer> map, char a, char b) {
if (map.get(a) >= map.get(b)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private int evaluate() {
int a = numStack.pollLast();
int b = numStack.pollLast();
char op = operatorStack.pollLast();
switch (op) {
case '+':
return a + b;
case '-':
return b - a;
case '*':
return a * b;
case '/':
return b / a;
default:
return 0;
}
}
}其他问题
剑指offerⅡ37:小行星碰撞
给定一个整数数组 asteroids,表示在同一行的小行星。
对于数组中的每一个元素,其绝对值表示小行星的大小,正负表示小行星的移动方向(正表示向右移动,负表示向左移动)。每一颗小行星以相同的速度移动。
找出碰撞后剩下的所有小行星。碰撞规则:两个行星相互碰撞,较小的行星会爆炸。如果两颗行星大小相同,则两颗行星都会爆炸。两颗移动方向相同的行星,永远不会发生碰撞。
示例 1:
输入:asteroids = [5,10,-5]
输出:[5,10]
解释:10 和 -5 碰撞后只剩下 10 。 5 和 10 永远不会发生碰撞。示例 2:
输入:asteroids = [8,-8]
输出:[]
解释:8 和 -8 碰撞后,两者都发生爆炸。示例 3:
输入:asteroids = [10,2,-5]
输出:[10]
解释:2 和 -5 发生碰撞后剩下 -5 。10 和 -5 发生碰撞后剩下 10 。示例 4:
输入:asteroids = [-2,-1,1,2]
输出:[-2,-1,1,2]
解释:-2 和 -1 向左移动,而 1 和 2 向右移动。 由于移动方向相同的行星不会发生碰撞,所以最终没有行星发生碰撞。算法:
class Solution {
public int[] asteroidCollision(int[] asteroids) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (int asteroid : asteroids) {
/**
这个题的逻辑很有意思:
按顺序扫描各个星球,
如果栈不为空,且栈顶为正(右),且此时的行星为负(左),且此时的行星更大,则弹出栈顶;循环继续判断。
如果跳出上面的循环,判断是什么条件跳出,再决定如何处理该行星。
1.如果栈不为空,且此时向左的行星与栈顶向右的行星一样大,则碰撞
2.如果栈为空,或此时的星球与栈顶的星球同向或相背飞行,此时的星球入栈
注意:以上并没有判断此时扫描的星球小于栈顶星球且碰撞的情形,此时扫描下一个星球即可。
*/
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.getLast() > 0 && asteroid < 0 && stack.getLast() < Math.abs(asteroid)) {
stack.pollLast();
}
if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.getLast() > 0 && asteroid < 0 && stack.getLast() == Math.abs(asteroid)) {
stack.pollLast();
} else if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.getLast() < 0 || asteroid > 0) {
stack.offer(asteroid);
}
//其他情况是该扫描的星球被撞毁,没有其他操作,只需要扫描下一个星球即可
}
return stack.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
}
}剑指offerⅠ9:两个栈实现队列
class CQueue {
Deque<Integer> stack1;
Deque<Integer> stack2;
public CQueue() {
stack1 = new LinkedList<>();
stack2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
stack1.offer(value);
}
public int deleteHead() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
int value = stack1.pollLast();
stack2.offer(value);
}
} else {
return stack2.pollLast();
}
return stack2.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack2.pollLast();
}
}LC155:包含min函数的栈
class MinStack {
/** initialize your data structure here. */
Deque<Integer> stack;
Deque<Integer> helper;
public MinStack() {
stack = new LinkedList<>();
helper = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.offer(x);
if (helper.isEmpty() || helper.peekLast() >= x) {
helper.offer(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
int num = stack.pollLast();
if (num == helper.peekLast()) {
helper.pollLast();
}
}
public int top() {
return stack.peekLast();
}
public int min() {
return helper.peekLast();
}
}LC946:栈的压入、弹出序列
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。**假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。**例如,序列 {1,2,3,4,5} 是某栈的压栈序列,序列 {4,5,3,2,1} 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 {4,3,5,1,2} 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int i = 0;
for (int num : pushed) {
stack.offer(num);
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peekLast() == popped[i]) {
stack.pollLast();
i++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}单调栈
剑指offerⅡ38:每日温度
请根据每日 气温 列表 temperatures ,重新生成一个列表,要求其对应位置的输出为:要想观测到更高的气温,至少需要等待的天数。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
示例 1:
输入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
输出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]示例 2:
输入: temperatures = [30,40,50,60]
输出: [1,1,1,0]示例 3:
输入: temperatures = [30,60,90]
输出: [1,1,0]算法:
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
Deque<Integer> stackIndex = new LinkedList<>();
int[] ans = new int[temperatures.length];
for (int i = 0; i < temperatures.length; i++) {
while (!stackIndex.isEmpty() && temperatures[stackIndex.getLast()] < temperatures[i]) {
int index = stackIndex.pollLast();
ans[index] = i - index;
}
stackIndex.offer(i);
}
return ans;
}
}剑指offerⅡ39:直方图最大矩形面积
给定非负整数数组 heights ,数组中的数字用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:
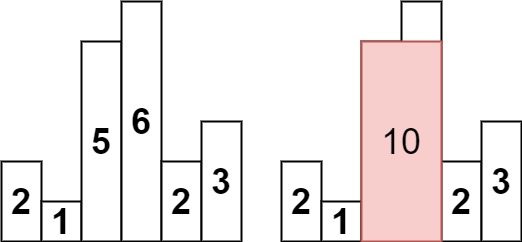
输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
输出:10
解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10方法一:暴力法
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {
int minHeight = heights[i];
for (int j = i; j < heights.length; j++) {
minHeight = Math.min(minHeight,heights[j]);
ans = Math.max(ans, minHeight * (j - i + 1));
}
}
return ans;
}
}该方法的时间复杂度为,不能通过该题的测试用例。
方法二:分治法
自己写的左闭右闭区间。因为刚开始没有分析·为左右边界的情况,导致minIndex±1会越界,所以加上这个判断条件。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
return helper(heights, 0, heights.length - 1);
}
private int helper(int[] heights, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) {
return heights[left];
}
int minIndex = left;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
if (heights[i] < heights[minIndex]) {
minIndex = i;
}
}
int ans = heights[minIndex] * (right - left + 1);
int leftArea = (minIndex == left) ? 0 : helper(heights, left, minIndex - 1);
int rightArea = (minIndex == right) ? 0 : helper(heights, minIndex + 1, right);
ans = Math.max(ans, leftArea);
return Math.max(ans, rightArea);
}
}左闭右开的方法:
注意进入helper函数时,需要判断两种特殊情况,如果left==right,表示空集;如果left+1==right,表示只有一个数。这种方法可以避免minIndex位于左右端点,进入下一层循环就会有left==right。
但是这种方法也不能通过这道题目。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
return helper(heights, 0, heights.length);
}
private int helper(int[] heights, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) {
return 0;
}
if (left + 1 == right) {
return heights[left];
}
int minIndex = left;
for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {
if (heights[i] < heights[minIndex]) {
minIndex = i;
}
}
int ans = heights[minIndex] * (right - left);
int leftArea = helper(heights, left, minIndex);
int rightArea = helper(heights, minIndex + 1, right);
ans = Math.max(ans, leftArea);
return Math.max(ans, rightArea);
}
}方法三:单调栈
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int area = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.offer(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {
/**
* 其实我觉得这里写成heights[i] < heights[stack.getLast()]更符合逻辑
* 如果当前栈为空,或者当前的height[i]大于等于栈顶存储的高度,则进栈
* 否则弹出当前栈顶,计算该值为高的矩形面积。该矩形的左边界为当前栈顶元素,右边界为扫描到的位置。
*/
while (stack.getLast() != -1 && heights[i] < heights[stack.getLast()]) {
int height = heights[stack.pollLast()];
int width = i - stack.getLast() - 1;
area = Math.max(area, height * width);
}
stack.offer(i);
}
/**
* 如果扫描完毕,栈还有剩下的元素,继续计算剩下的可能
* 以弹出栈顶元素为矩形的高,矩形的宽为heights.length - stack.getLast() - 1
*/
while (stack.getLast() != -1) {
int height = heights[stack.pollLast()];
int width = heights.length - stack.getLast() - 1;
area = Math.max(area, height * width);
}
return area;
}
}剑指offerⅡ40:矩阵中最大的矩形
给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵 matrix ,找出只包含 1 的最大矩形,并返回其面积。
**注意:**此题 matrix 输入格式为一维 01 字符串数组。
class Solution {
public int maximalRectangle(String[] matrix) {
int area = 0;
if (matrix.length == 0) {
return area;
}
int[] heights = new int[matrix[0].length()];
for (String str : matrix) {
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) == '0') {
heights[i] = 0;
} else {
heights[i]++;
}
}
area = Math.max(area, largestRectangleArea(heights));
}
return area;
}
private int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int area = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.offer(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {
while (stack.getLast() != -1 && heights[i] < heights[stack.getLast()]) {
int height = heights[stack.pollLast()];
int width = i - stack.getLast() - 1;
area = Math.max(area, height * width);
}
stack.offer(i);
}
while (stack.getLast() != -1) {
int height = heights[stack.pollLast()];
int width = heights.length - stack.getLast() - 1;
area = Math.max(area, height * width);
}
return area;
}
}