第4章 链表
双指针
剑指offerⅡ21:删除倒数第n个节点
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = dummy;
while (n > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
n--;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}剑指offerⅡ22:链表中环的入口节点
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 从链表的头节点开始沿着 next 指针进入环的第一个节点为环的入口节点。如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
**说明:**不允许修改给定的链表。
方法一:Set存储访问过的节点,再次访问则为循环的入口;如果访问到了根节点,说明没有环,返回null。击败了14%,5%.
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null) {
if (set.contains(head)) {
return head;
}
set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return null;
}
}方法二:需要知道环中节点数目的解法:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode nodeInLoop = getNodeInLoop(head);
if (nodeInLoop == null) {
return null;
}
int loopNum = 1;
//计算环中节点数
for (ListNode cur = nodeInLoop.next; cur != nodeInLoop; cur = cur.next, loopNum++) ;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
//快指针先走环中节点数的步数
for (; loopNum > 0; loopNum--, fast = fast.next) ;
//一起走,相遇则是入口
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
//找到环中任意一个节点
private ListNode getNodeInLoop(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
//这里不能将二者都赋值为head,否则进入while直接返回
ListNode fast = head.next.next;
ListNode slow = head.next;
while (fast != null) {
if (fast == slow) {
return fast;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}方法三:不需要知道环中节点数目的解法:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode nodeInLoop = getNodeInLoop(head);
if (nodeInLoop == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode node = head;
while (node != nodeInLoop) {
node = node.next;
nodeInLoop = nodeInLoop.next;
}
return node;
}
//找到环中任意一个节点
private ListNode getNodeInLoop(ListNode head) {
/**省略**/
}
}在相遇之前,快指针走了2k步,慢指针走了k步。除去两者走的相同的部分,剩下的部分一定是走了环的圈,所以k是环的整数倍,那么慢指针也走了环的整数倍。接下来让node从头节点开始走,另一个节点从此时的慢指针开始走,两者相遇的位置即为环的起始。
剑指offerⅡ23:两个链表的第一个重合的节点
给定两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
也有可能没有交点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode h1 = headA, h2 = headB;
while (h1 != h2) {
h1 = (h1 == null) ? headB : h1.next;
h2 = (h2 == null) ? headA : h2.next;
}
return h1;
}
}反转链表
剑指offerⅡ24:反转链表
非递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
}递归:
剑指offerⅡ25:链表中数字相加
给定两个 非空链表 l1和 l2 来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head1 = reverseList(l1);
ListNode head2 = reverseList(l2);
ListNode head = addList(head1, head2);
return reverseList(head);
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
private ListNode addList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int carry = 0;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int num1 = (l1 != null) ? l1.val : 0;
int num2 = (l2 != null) ? l2.val : 0;
int num = (num1 + num2 + carry) % 10;
carry = (num1 + num2 + carry) / 10;
ListNode node = new ListNode(num);
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
l1 = (l1 == null) ? null : l1.next;
l2 = (l2 == null) ? null : l2.next;
}
cur.next = (carry > 0) ? new ListNode(carry) : null;
return dummy.next;
}
}该题代码的风格,和面试题2很像,可以反比对比、反复练习、反复记忆、反复断气。
剑指offerⅡ26:重排链表
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln-1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln-1 → L2 → Ln-2 → …不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
自己写的代码:
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return;
}
ListNode secondeHead = getSecondList(head);
secondeHead = reverseList(secondeHead);
System.out.println(secondeHead.val);
ListNode cur = head;
while (secondeHead != null) {
ListNode nextFirst = cur.next;
ListNode nextSecond = secondeHead.next;
cur.next = secondeHead;
secondeHead.next = nextFirst;
cur = nextFirst;
secondeHead = nextSecond;
}
}
private ListNode getSecondList(ListNode head) {
ListNode slowPrev = head;
ListNode slow = head.next;
ListNode fast = slow.next;
while (fast != null) {
slowPrev = slowPrev.next;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
slowPrev.next = null;
return slow;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
}书上的代码:
剑指offerⅡ27:回文链表
给定一个链表的 头节点 head **,**请判断其是否为回文链表。
如果一个链表是回文,那么链表节点序列从前往后看和从后往前看是相同的。
示例 1:
输入: head = [1,2,3,3,2,1]
输出: true示例 2:
输入: head = [1,2]
输出: false提示:
- 链表 L 的长度范围为
[1, 105] 0 <= node.val <= 9
**进阶:**能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode h1 = head;
ListNode h2 = split(head);
h2 = reverse(h2);
while (h2 != null) {
if (h1.val != h2.val) {
return false;
}
h1 = h1.next;
h2 = h2.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode split(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode second = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
return second;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
}双向链表和循环列表
剑指offerⅡ28:展平多级双向链表
多级双向链表中,除了指向下一个节点和前一个节点指针之外,它还有一个子链表指针,可能指向单独的双向链表。这些子列表也可能会有一个或多个自己的子项,依此类推,生成多级数据结构,如下面的示例所示。
给定位于列表第一级的头节点,请扁平化列表,即将这样的多级双向链表展平成普通的双向链表,使所有结点出现在单级双链表中。
方法一:迭代法
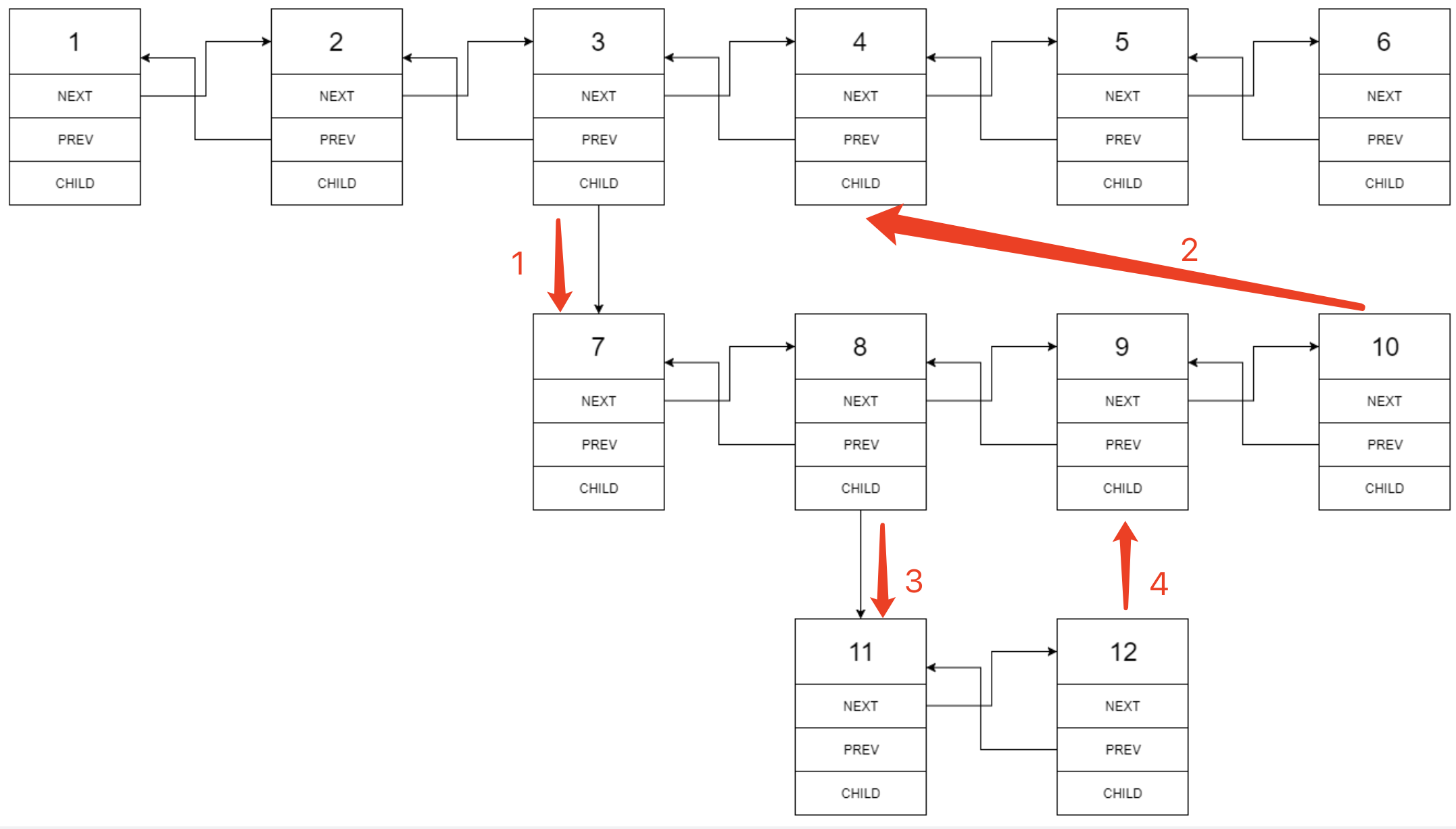
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.child != null) {
Node next = cur.next;
Node child = cur.child;
child.prev = cur;
cur.next = child;
cur.child = null;
Node last = child;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;//找到这一级最后一个节点
}
last.next = next;
if (next != null) {
next.prev = last;//如果next不是null节点,则它的前驱节点指向last节点
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}方法二:递归法
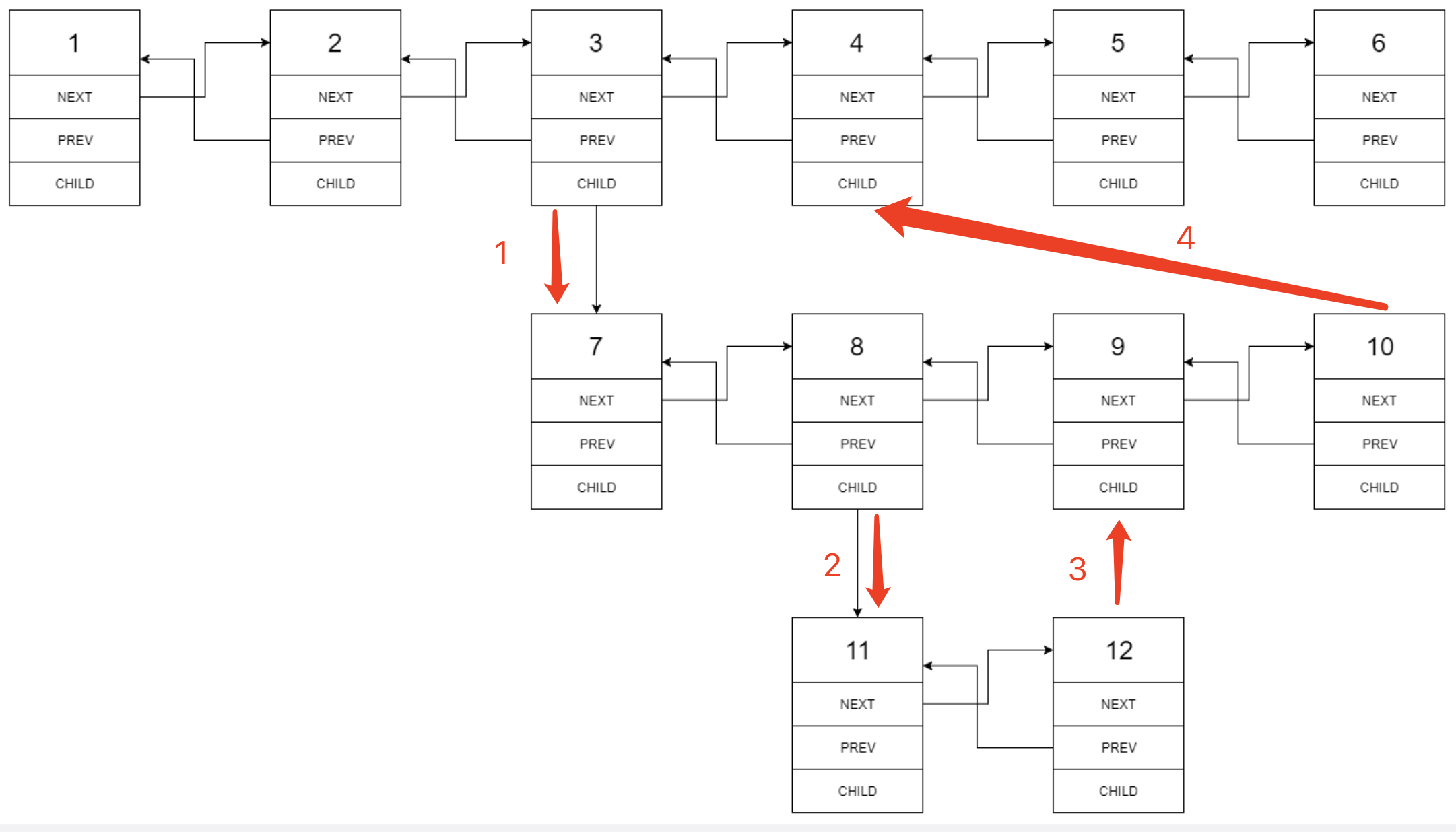
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
Node dummy = new Node();
dummy.next = head;
while (head != null) {
if (head.child == null) {
head = head.next;
} else {
Node tmp = head.next;
Node chead = flatten(head.child);
head.next = chead;
chead.prev = head;
head.child = null;
while (head.next != null) head = head.next;
head.next = tmp;
if (tmp != null) tmp.prev = head;
head = tmp;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}方法三:递归法优化版
在上述解法中,由于我们直接使用 flatten 作为递归函数,导致递归处理 后不得不再进行遍历来找当前层的“尾结点”,这导致算法复杂度为 。
一个可行的优化是,额外设计一个递归函数 getTail 用于返回扁平化后的链表**“尾结点”**,从而确保我们找尾结点的动作不会在每层发生。
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
getTail(head);
return head;
}
//找到本级的尾节点
private Node getTail(Node head) {
Node tail = head;
Node node = head;
while (node != null) {
if (node.child == null) {
tail = node;
node = node.next;
} else {
Node next = node.next;
Node flattenTail = getTail(node.child);
node.next = node.child;
node.child.prev = node;
node.child = null;
flattenTail.next = next;
if (next != null) {
next.prev = flattenTail;
}
tail = flattenTail;
node = next;
}
}
return tail;
}
}剑指offerⅡ29:排序的循环链表
给定循环升序列表中的一个点,写一个函数向这个列表中插入一个新元素 insertVal ,使这个列表仍然是循环升序的。
给定的可以是这个列表中任意一个顶点的指针,并不一定是这个列表中最小元素的指针。
如果有多个满足条件的插入位置,可以选择任意一个位置插入新的值,插入后整个列表仍然保持有序。
如果列表为空(给定的节点是 null),需要创建一个循环有序列表并返回这个节点。否则。请返回原先给定的节点。
解题思路:
class Solution {
public Node insert(Node head, int insertVal) {
Node node = new Node(insertVal);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
head.next = head;
} else if (head.next == head) {
head.next = node;
node.next = head;
} else {
insertNode(node, head);
}
return head;
}
public void insertNode(Node node, Node head) {
Node max = head;
Node next = head.next;
Node cur = head;
while (next != head && !(cur.val <= node.val && node.val <= next.val)) {
cur = next;
next = next.next;
if (max.val <= cur.val) {//这里必须是<=,考虑到测试用例[1,3,3]
max = cur;
}
}
if (cur.val <= node.val && node.val <= next.val) {
cur.next = node;
node.next = next;
} else {
node.next = max.next;
max.next = node;
}
}
}LC138:复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:

输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]方法一:哈希表
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}方法二:拼接 + 拆分
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while (cur != null) {
Node temp = new Node(cur.val);
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
cur = temp.next;
}
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.random != null) {
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3. 拆分两链表
Node ans = head.next, pre = head;
cur = head.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
//这里先修改pre再修改cur
//同时必须恢复原链表
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null;// 单独处理原链表尾节点
return ans;
}
}